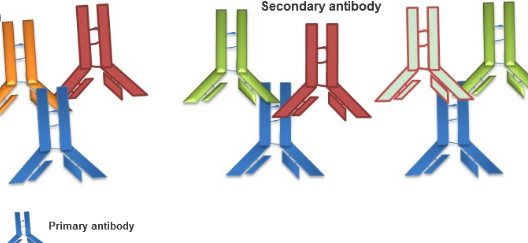
Antibodies that are used in research for the detection of antigens in biochemical, cell biology or histological tests, among others, can be classified as primary or secondary depending on their binding capacity and their application.
In this entry we analyze the main 5 differences between primary and secondary antibodies that will help us select the most appropriate reagent for our immunoassay.
1.- JOINING CAPACITY
- Primary Antibodies : Bind directly to the antigen by recognizing a specific epitope on it.
- Secondary Antibodies : Bind to a primary antibody, specifically the Fc region thereof. This Fc domain is the same for all the antibodies of the same class in a given species, so the same secondary antibody will be able to bind different types of primary antibodies.
2.- SOURCE OF OBTAINING
- Primary Antibodies : The host or organism in which a primary antibody is obtained must be of a different species than the study sample.
- Secondary Antibodies : The host in which a secondary antibody is generated must be of a different species from the host in which the primary antibody was obtained to guarantee reactivity against it.
3.- USE OF ANTIBODIES
- Primary Antibodies : The use of a primary antibody is essential in any immunoassay for the detection of the antigen of interest.
- Secondary antibodies : They are only necessary in certain immunoassays in which signal amplification is required or in which it is not possible to label the primary antibody for detection.
4.- MARKING
- Primary Antibodies : They are only marked in the case of direct immunoassays for their direct detection.
- Secondary antibodies : They should always be marked since their function is the detection and amplification of the signal.
5.- CLONALITY
- Primary antibodies : They can be both monoclonal and polyclonal depending on the application for which they are intended. The monoclonal ones provide specificity and reproducibility while the polyclonal ones offer greater sensitivity .
- Secondary antibodies : Although secondary antibodies can also be monoclonal or polyclonal, the selection of the latter is much more frequent since they allow the binding of several secondary antibodies to the same primary antibody, thus achieving greater signal amplification.