Brugada syndrome (BrS) is a genetic situation that accentuates the danger of doubtless deadly ventricular arrhythmias and sudden cardiac dying (SCD) in a structurally regular coronary heart. The Brugada electrocardiographic sample might manifest individually from the syndrome-this medical state of affairs has been described as Brugada phenocopy (BrP).
Many etiologies of BrP have been reported, however it has not but been reported because of coronary gradual movement (CSF) phenomenon.
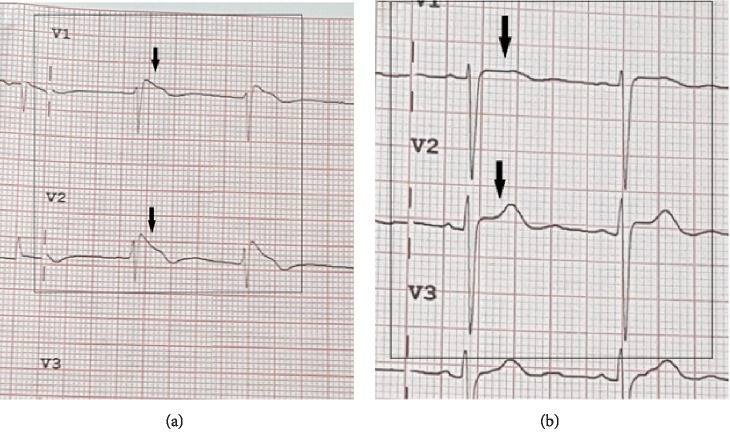
This case report highlights a suspected coronary gradual flow-associated Brugada sort 1 electrocardiographic sample, which subsequently normalized following the establishment of guideline-directed medical remedy for acute coronary syndrome.
The Genetic Landscape of Arab Population, Chechens and Circassians Subpopulations from Jordan by HV1 and HV2 areas of mtDNA.
The skill to noninvasively monitor retinal abnormalities utilizing imaging and cognitive and electrophysiological evaluation has made it doable to fastidiously characterize genetic influences on retinal well being.
Because genetic retinal traits in animal species usually are not generally detrimental to survival past start, it’s doable to doc the pure historical past of retinal illness. Human high quality of life is drastically impacted by retinal illness, and blindness carries a major monetary burden to society. Because of those compelling causes, there’s an ongoing medical want to examine the impact of genetic mutations on retinal well being and to develop therapies to deal with them.
Transgenic animal fashions have aided in these missions, however there are alternatives for novel gene discovery and a improvement of higher understanding of retinal physiology utilizing animal fashions that develop naturally occurring heritable retinal issues.
In this chapter, the benefits and downsides of transgenic and spontaneous vertebrate animal fashions of human inherited retinal illness are debated, particularly these of carnivore species, and the potential useful resource of spontaneous heritable retinal issues in inbred nondomestic carnivore species is mentioned.
Beta-caryophyllene, a dietary terpenoid, inhibits nicotine-taking and nicotine-seeking in rodents.
Beta-caryophyllene (BCP) is a dietary plant-derived terpenoid that has been used as a meals additive for a lot of a long time.
Recent research point out that BCP is a cannabinoid CB2 receptor (CB2R) agonist with medical advantages for various human ailments. However, little is understood about its therapeutic potential for drug abuse and habit.We used pharmacological, transgenic, and optogenetic approaches to systematically consider the results of BCP on nicotine-taking and nicotine-seeking conduct in animal fashions of drug self-administration, electrical and optical brain-stimulation reward.
Systemic administration of BCP dose-dependently inhibited nicotine self-administration and motivation for nicotine searching for in rats and mice. The discount in nicotine self-administration was blocked by AM630, a selective CB2R antagonist, however not by AM251, a selective CB1R antagonist, suggesting the involvement of a CB2R mechanism.
Genetic deletion of CB2Rs in CB2-knockout mice blocked the discount in nicotine self-administration produced solely by low doses, however not excessive doses, of BCP, suggesting the involvement of each CB2 and non-CB2 receptor mechanisms. Furthermore, within the intracranial self-stimulation paradigm, BCP attenuated electrical brain-stimulation reward (BSR) and nicotine-enhanced BSR in rats. Lastly, BCP additionally attenuated BSR maintained by optogenetic stimulation of dopamine (DA) neurons within the ventral tegmental space in DAT-cre mice, suggesting the involvement of a DA-dependent mechanism in BCP’s motion.
The current findings counsel that BCP has important anti-nicotine results by way of each CB2 and non-CB2 receptor mechanisms, and subsequently, deserves additional examine as a possible new pharmacotherapy for cigarette smoking cessation.
